With astronomy ranking task the seasons at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights. The ranking of seasons in astronomy is a captivating concept that delves into the intricacies of celestial events and their impact on our planet.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the criteria used to rank the seasons, explore the astronomical phenomena that occur during each season, and discover the practical applications of these rankings in astronomy.
Seasonal phenomena, observed and measured with precision, provide valuable insights into the rhythmic patterns of our planet. From the celestial dance of solstices and equinoxes to the subtle shifts in star patterns, each season unveils a unique tapestry of astronomical events.
By harnessing statistical techniques and data visualization, astronomers unravel the complexities of these phenomena, enabling us to rank the seasons based on their distinct characteristics.
Astronomy Ranking Task: The Seasons

The astronomy ranking task involves ranking the seasons based on their astronomical characteristics and observable phenomena. This task is significant as it provides a framework for understanding the seasonal variations in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and their impact on various astronomical observations.
The criteria used to rank the seasons include:
- Duration of daylight and darkness
- Solar altitude and zenith
- Star visibility and constellation patterns
- Temperature and weather patterns
Seasonal Phenomena and Observations
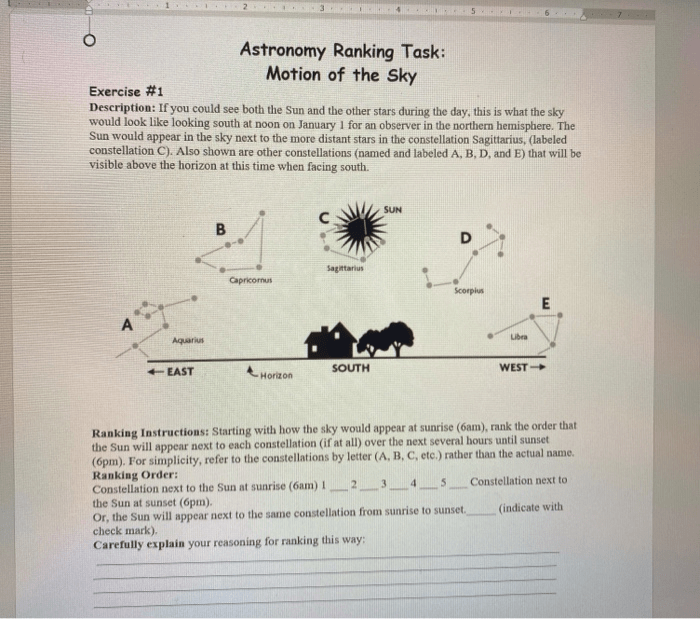
Each season is characterized by distinct astronomical phenomena that can be observed and measured. These phenomena include:
Spring
- Increasing daylight hours
- Higher solar altitude
- Vernal equinox (day and night of equal length)
- Appearance of specific constellations (e.g., Ursa Major, Leo)
Summer, Astronomy ranking task the seasons
- Longest daylight hours
- Highest solar altitude
- Summer solstice (longest day of the year)
- Prominent summer constellations (e.g., Cygnus, Lyra)
Autumn
- Decreasing daylight hours
- Lower solar altitude
- Autumnal equinox (day and night of equal length)
- Appearance of autumn constellations (e.g., Pegasus, Andromeda)
Winter
- Shortest daylight hours
- Lowest solar altitude
- Winter solstice (shortest day of the year)
- Dominance of winter constellations (e.g., Orion, Taurus)
Data Collection and Analysis
Data on seasonal phenomena can be collected through various methods, including:
- Observational data (e.g., sunrise and sunset times, star visibility)
- Meteorological data (e.g., temperature, precipitation)
- Astronomical data (e.g., solar altitude, equinox and solstice dates)
Statistical techniques are used to analyze the data and rank the seasons. These techniques include:
- Descriptive statistics (e.g., mean, median, standard deviation)
- Regression analysis (e.g., linear regression, multiple regression)
- Time series analysis (e.g., autocorrelation, moving averages)
Data visualization techniques, such as graphs and charts, are used to present the results of the analysis and compare the seasons.
Applications of Seasonal Rankings
Seasonal rankings have practical applications in astronomy, including:
- Understanding climate patterns and long-term climate trends
- Predicting weather events and seasonal variations
- Planning space missions and astronomical observations
- Determining optimal times for astronomical observations (e.g., meteor showers, eclipses)
For example, knowing the ranking of seasons based on solar altitude can help astronomers predict the best time for solar observations and the optimal conditions for observing specific solar phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions: Astronomy Ranking Task The Seasons
What is the purpose of the astronomy ranking task the seasons?
The astronomy ranking task the seasons aims to establish a systematic framework for comparing and ranking the seasons based on their distinct astronomical phenomena and their impact on our planet.
How are the seasons ranked in astronomy?
Seasons are ranked in astronomy using a set of criteria that consider the astronomical phenomena that occur during each season, such as the position of the Earth in its orbit, the duration of daylight, and the intensity of solar radiation.
What are some examples of astronomical phenomena that are used to rank the seasons?
Examples of astronomical phenomena that are used to rank the seasons include solstices, equinoxes, and the changing positions of constellations in the night sky.
