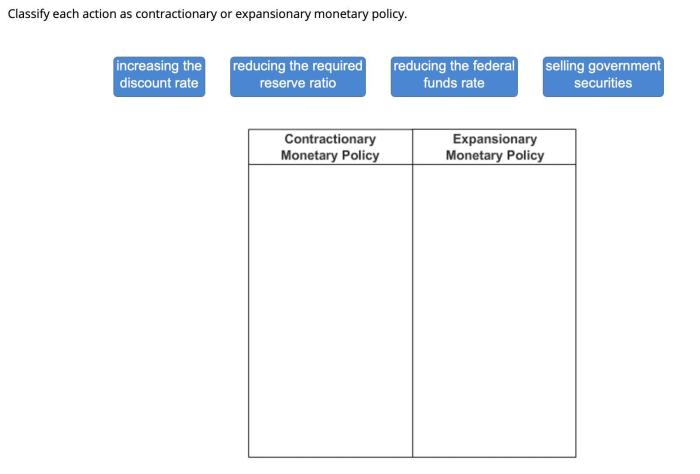
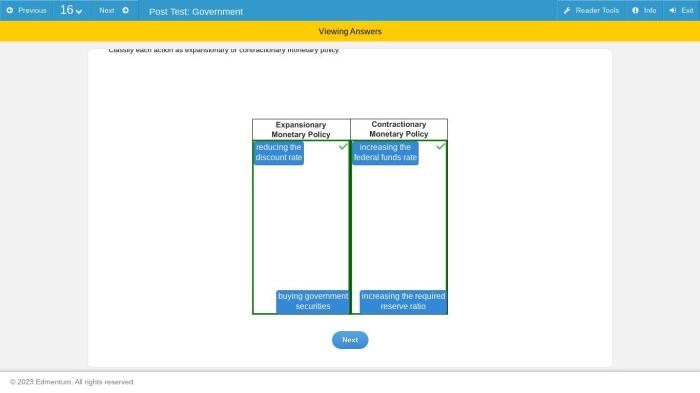
Classify each action as contractionary or expansionary monetary policy. – Monetary policy, a crucial tool for economic management, encompasses actions taken by central banks to influence the money supply and economic activity. This article aims to clarify the distinction between contractionary and expansionary monetary policies, exploring their specific actions and economic implications.
Contractionary monetary policy involves measures that reduce the money supply, typically employed to combat inflation or excessive economic growth. Conversely, expansionary monetary policy aims to increase the money supply, often used to stimulate economic activity or combat recession.
Monetary Policy Definitions: Classify Each Action As Contractionary Or Expansionary Monetary Policy.
Monetary policy refers to the set of actions taken by a central bank to influence the money supply and interest rates within an economy. It aims to maintain economic stability, promote growth, and control inflation.Contractionary monetary policy involves measures that reduce the money supply and increase interest rates, while expansionary monetary policy involves actions that increase the money supply and decrease interest rates.
Contractionary Monetary Policy Actions
Contractionary monetary policy aims to reduce inflation or slow down economic growth by reducing the money supply and increasing interest rates. Specific actions that constitute contractionary monetary policy include:
- Open market operations:Selling government securities to reduce the money supply.
- Raising reserve requirements:Increasing the amount of reserves banks are required to hold, reducing their ability to lend.
- Increasing the discount rate:The interest rate charged to banks for borrowing from the central bank, discouraging borrowing and lending.
- Quantitative tightening:Reducing the size of the central bank’s balance sheet by selling assets.
Expansionary Monetary Policy Actions, Classify each action as contractionary or expansionary monetary policy.
Expansionary monetary policy aims to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation by increasing the money supply and decreasing interest rates. Specific actions that constitute expansionary monetary policy include:
- Open market operations:Buying government securities to increase the money supply.
- Lowering reserve requirements:Decreasing the amount of reserves banks are required to hold, increasing their ability to lend.
- Lowering the discount rate:Reducing the interest rate charged to banks for borrowing from the central bank, encouraging borrowing and lending.
- Quantitative easing:Increasing the size of the central bank’s balance sheet by purchasing assets.
Helpful Answers
What is the primary goal of contractionary monetary policy?
To reduce inflation or curb excessive economic growth by decreasing the money supply.
How does expansionary monetary policy stimulate economic activity?
By increasing the money supply, making borrowing more accessible and encouraging investment and spending.
What factors do policymakers consider when implementing monetary policy?
Economic growth, inflation, unemployment, and financial stability, among others.